You can use Android Debug Bridge (ADB) to connect your Fire tablet to your computer for testing and debugging. You connect your computer to your Fire tablet through a micro-USB cable.
USB to serial drivers for most serial RS232 devices. Download drivers for most types of USB to serial adapters and converters. X1de-usb driver – Iomega BXXU0130 144MB USB Floppy Disk Drive (SilverBlack) (BXXU0130) Floppy Drive. But any floppy I put in it is listed as iomegaa or unreadable. Sexually explicit or offensive language. Makes the device visible and I have a device A: Iomega StorCenter ix2 GB Looking for a solution to this for months.
Android Debug Bridge (ADB) is a command-line utility for running and managing Android apps on your device or emulator. For more information and instructions on using ADB, see Android Debug Bridge.
If you're looking for instructions on connecting to a Fire TV instead, see Connect to Fire TV Through ADB.
- Check for Device Connections Using ADB (Optional)
- Troubleshooting
Step 1: Enable Developer Options
Go to Settings > Device Options and look for a Developer Options menu. If it's not there, do the following:
a. Go to Settings > Device Options > About Fire Tablet.b. Tap your Serial Number seven times.c. Return to Device Options. A new menu appears called 'Developer Options.'
- Tap Developer options. (2013 models might call this option 'Security.')
- Set Developer options and USB debugging to ON.
- If you have a Kindle Fire 1st Generation, ADB is enabled by default.
Step 2: Install the Kindle Fire Driver (Windows Only)
- If you're using Windows, download this Kindle Fire driver: kindle_fire_usb_driver.zip.
- After downloading the file, extract the contents into a new folder and double-click the Fire_Devices ABD drivers file.
- Proceed through the installation wizard screens to install the driver.
Step 3: Install Android Studio
ADB is available on your computer when you install Android Studio. If you don't already have Android Studio, download and install Android Studio. If you're not using Android Studio, you need to download and install Android SDK platform tools.
Omega USB Devices Driver
Step 4: Connect Your Fire Device to Your Computer with a USB Cable
Using a USB cable, connect your Fire tablet to a USB port on your computer.
Note that Fire tablets can treat the USB with different transfer options. After connecting the USB cable, swipe down from the top of your tablet to see the USB option used. You might see various notifications, including the USB connection type that was used when you connected the cable. The relevant notification is highlighted in the screenshot below.
If you don't see 'Connected as Media Device', press Tap for other USB options. Then select Media device (MTP). Later Fire OS versions have a different interface here. If you're using Fire OS 7, select File Transfer.
Note: If your USB is connected as a Camera (PTP), Android Studio won't recognize the tablet as a device in Android Studio.If you don't see the USB connection type in the above notifications, go to Settings > Device Options > Developer Options > USB computer connection. Set this to Media device (MTP). For Fire OS 7, select File Transfer.
When the Allow USB debugging? dialog appears on your tablet, tap OK.
Open Android Studio and look for the device to appear in devices drop-down menu:
The device's name will use the
android.os.Build.MODELproperty for the device.KFSUWIrefers to Fire HD 10 (2017) tablet. You can see a list of build model names in the Identifying Fire Tablet Devices.If you have not selected the 'Allow USB Debugging' dialog on your tablet, the name 'Unknown device' will appear in the devices drop-down menu in Android Studio until you allow debugging.
With the tablet connected, you can now run your app on your tablet by clicking the Run App button in Android Studio.
If you run into issues, see the Troubleshooting section below.
Check for Device Connections Using ADB (Optional)
Instead of looking in the devices menu in Android Studio, you can also use some ADB terminal commands to confirm that your device is connected. ADB is useful for performing many other operations as well, such as entering sandbox mode or installing other assets. Follow these two sections:
If you skip adding ADB to your PATH, you can also Check for Connected Devices If ADB Isn't In Your PATH.
Add ADB to Your PATH
First, add ADB to your PATH so you can more easily run ADB commands. (Your PATH is an environment variable used to specify the location of the program's executable. If you don't add ADB to your PATH, running ADB commands will require you to browse to the <Android SDK>/platform-tools directory to run adb.)
adb version from a terminal or command prompt. If you get back version information, then ADB is in your PATH. If the response says adb is an unrecognized command, ADB is not in your PATH.To add ADB to your PATH on Mac:
Get the path to your Android SDK platform-tools directory:
Open Android Studio and click the SDK Manager button .The location to your Android SDK appears near the top next to Android SDK Location. For example:
/Users/<your username>/Library/Android/sdkIf this is your first time opening Android Studio, there isn't an SDK Manager button. Instead, at the Welcome to Android Studio prompt, click Configure > SDK Manager and provide the location to the Android SDK.
- Copy the path to the SDK and paste it somewhere convenient, such as a text editor.
- Add /platform-tools to the end of the path you copied in the previous step. ('platform-tools' is the directory containing the ADB executable.)
- Copy the full path to your clipboard.
Use the following command to add ADB to your .bash_profile. Replace
<your username>with your actual username. Also, make sure the path points to your Android SDK.Your
.bash_profilefile is usually in your user directory, which you can find by typingcd ~(change to your user directory). Then typels -a(list all) to show all files, including hidden ones.If the file isn't there, simply create one. You can then type
open .bash_profileto see the paths listed.After you add this PATH to your bash profile, you should see the following in your
.bash_profilefile:(Only instead of
johndoe, you will see your own username.)Fully restart any terminal sessions, and then type
adb. If you successfully added ADB to your path, you will see ADB help info rather than 'command not found.'
To add ADB to your PATH on Windows:
Get the path to your Android SDK platform-tools directory:
Open Android Studio and click the SDK Manager button .
The location to your Android SDK appears near the top next to Android SDK Location. For example:
C:Users<your user name>AppDataLocalAndroidSdkIf this is your first time opening Android Studio, there isn't an SDK Manager button. Instead, at the Welcome to Android Studio prompt, click Configure > SDK Manager and provide the location to the Android SDK.
- Copy the path to the SDK and paste it somewhere convenient, such as a text editor.
- Add /platform-tools to the end of the path you copied in the previous step. ('platform-tools' is the directory containing the ADB executable.)
- Copy the full path to your clipboard.
- Click your computer's search button (next to Start) and type view advanced system settings.
- Click View advanced system settings.
- When the System Settings dialog opens, click the Environment Variables button.
- Under System Variables (the lower pane), select Path and click Edit.
Do one of the following:
- On Windows 7 or 8, move your cursor to the farthest position on the right, type
;and then press Ctrl+V to insert the path to your SDK that you copied earlier. It may look like this:;C:Users<your user name>AppDataLocalAndroidSdkplatform-tools. Click OK on each of the three open dialog boxes to close them. - On Windows 10, click the New button and add this location.
- On Windows 7 or 8, move your cursor to the farthest position on the right, type
- Restart any terminal sessions, and then type
adb. If you successfully added ADB to your path, you will see ADB help info rather than 'command not found.'
Check for Connected Devices
Assuming ADB is added to your PATH, run the following commands:
Confirm that the serial number for your Fire tablet appears in the list of devices. For example:
On your tablet, your device's serial number is located under Settings > Device Options.
Check for Connected Devices If ADB Isn't In Your PATH
If your terminal doesn't recognize adb as a command (that is, you didn't add ADB to your PATH), you might have to run the commands from the SDK directory that contains ADB.
- In Android Studio go to Tools > SDK Manager.
- In the SDK Manager dialog box, copy the Android SDK Location.
Browse to this location in your terminal or command prompt. For example:
Mac
Windows
Then go into the
platform-toolsdirectory:The
platform-toolsdirectory containsadb.Now run the ADB commands as follows:
Mac:
Windows:
The response should list your device's serial number. For example:
If your Fire tablet is still not detected, you may need to reboot your computer or log out and back in for the changes to take effect.
Troubleshooting
Tablet doesn't appear in list of devices in Android Studio
If you don't see your tablet device in the list of devices in Android Studio, click the devices drop-down menu and select Troubleshoot device connections:
Click Rescan devices.
If rescanning devices doesn't detect your Fire tablet as a device, your micro-USB cable might be bad, you might have the wrong USB connection type (e.g, camera instead of media device), or you might not have enabled USB debugging. You can also try restarting your computer and the tablet.
Uninstall the non-ADB Driver (Windows)
If you previously connected a Fire tablet without first enabling ADB on the Fire tablet, you might need to remove the existing USB device driver and force re-installation of the driver. To remove the non-ADB driver:
- Using a micro-USB cable, connect your Fire tablet to a USB port on your computer.
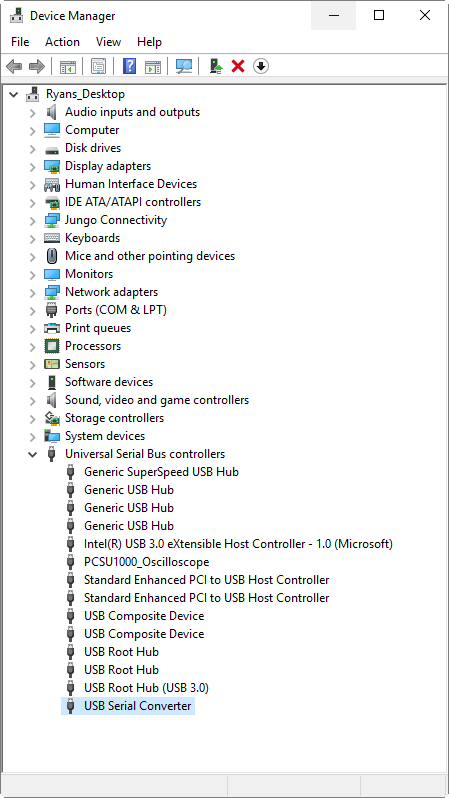
- On your computer (Windows 10), click the search button (next to the Start menu) and type Device Manager in the search. Then select it in the results. (Other Windows versions have different options for accessing the Control Panel.)
- In the Device Manager window, expand Portable Devices.
- Right-click the Fire device and then click Properties.
- In the Properties window, on the Driver tab, click Uninstall, and then Confirm.
- Unplug your Fire tablet from your computer.
Confirm the Fire Driver Is Installed Correctly
You can confirm that the Fire driver is installed correctly by doing the following:
- On your computer, click the search button search button (next to the Start menu) and type Device Manager.
In Device Manager, under Fire Devices, verify that that a device appears called Android Composite ADB Interface.
If your Device Manager shows an Other Devices section with a second Fire device with a yellow alert sign, your computer is listing Amazon's unrecognized ADB module as a separate device. To fix this issue:
- Under Other Devices, right-click the Fire device and select Properties.
- On the Driver tab of the Properties window, select Update Driver…
- Choose to browse for the driver software, then navigate to Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer > Show All Devices > Have Disk.
- Navigate to the folder where you installed the Amazon driver (typically
C:Program Files (x86)Amazon.comFire_DevicesDrivers) and select it. Ignore the warning regarding installing drivers and proceed.
You should now correctly see your Fire tablet with the ADB driver installed.
Last updated: Oct 29, 2020
-->For certain Universal Serial Bus (USB) devices, such as devices that are accessed by only a single application, you can install WinUSB (Winusb.sys) in the device's kernel-mode stack as the USB device's function driver instead of implementing a driver.
This topic contains these sections:
Automatic installation of WinUSB without an INF file
As an OEM or independent hardware vendor (IHV), you can build your device so that the Winusb.sys gets installed automatically on Windows 8 and later versions of the operating system. Such a device is called a WinUSB device and does not require you to write a custom INF file that references in-box Winusb.inf.
When you connect a WinUSB device, the system reads device information and loads Winusb.sys automatically.
For more information, see WinUSB Device.
Installing WinUSB by specifying the system-provided device class
When you connect your device, you might notice that Windows loads Winusb.sys automatically (if the IHV has defined the device as a WinUSB Device). Otherwise follow these instructions to load the driver:
Omega Usb Devices Drivers
- Plug in your device to the host system.
- Open Device Manager and locate the device.
- Select and hold (or right-click) the device and select Update driver software... from the context menu.
- In the wizard, select Browse my computer for driver software.
- Select Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer.
- From the list of device classes, select Universal Serial Bus devices.
- The wizard displays WinUsb Device. Select it to load the driver.
If Universal Serial Bus devices does not appear in the list of device classes, then you need to install the driver by using a custom INF.The preceding procedure does not add a device interface GUID for an app (UWP app or Windows desktop app) to access the device. You must add the GUID manually by following this procedure.
Load the driver as described in the preceding procedure.
Generate a device interface GUID for your device, by using a tool such as guidgen.exe.
Find the registry key for the device under this key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetEnumUSB<VID_vvvv&PID_pppp>
Under the Device Parameters key, add a String registry entry named DeviceInterfaceGUID or a Multi-String entry named DeviceInterfaceGUIDs. Set the value to the GUID you generated in step 2.
Disconnect the device from the system and reconnect it to the same physical port.Note If you change the physical port then you must repeat steps 1 through 4.
Writing a custom INF for WinUSB installation
As part of the driver package, you provide an .inf file that installs Winusb.sys as the function driver for the USB device.
The following example .inf file shows WinUSB installation for most USB devices with some modifications, such as changing USB_Install in section names to an appropriate DDInstall value. You should also change the version, manufacturer, and model sections as necessary. For example, provide an appropriate manufacture's name, the name of your signed catalog file, the correct device class, and the vendor identifier (VID) and product identifier (PID) for the device.
Also notice that the setup class is set to 'USBDevice'. Vendors can use the 'USBDevice' setup class for devices that do not belong to another class and are not USB host controllers or hubs.
If you are installing WinUSB as the function driver for one of the functions in a USB composite device, you must provide the hardware ID that is associated with the function, in the INF. You can obtain the hardware ID for the function from the properties of the devnode in Device Manager. The hardware ID string format is 'USBVID_vvvv&PID_pppp'.
The following INF installs WinUSB as the OSR USB FX2 board's function driver on a x64-based system.
Starting in Windows 10, version 1709, the Windows Driver Kit provides InfVerif.exe that you can use to test a driver INF file to make sure there are no syntax issues and the INF file is universal. We recommened that you provide a universal INF. For more information, see Using a Universal INF File.
Only include a ClassInstall32 section in a device INF file to install a new custom device setup class. INF files for devices in an installed class, whether a system-supplied device setup class or a custom class, must not include a ClassInstall32 section.
Except for device-specific values and several issues that are noted in the following list, you can use these sections and directives to install WinUSB for any USB device. These list items describe the Includes and Directives in the preceding .inf file.
USB_Install: The Include and Needs directives in the USB_Install section are required for installing WinUSB. You should not modify these directives.
USB_Install.Services: The Include directive in the USB_Install.Services section includes the system-supplied .inf for WinUSB (WinUSB.inf). This .inf file is installed by the WinUSB co-installer if it isn't already on the target system. The Needs directive specifies the section within WinUSB.inf that contains information required to install Winusb.sys as the device's function driver. You should not modify these directives.Note Because Windows XP doesn't provide WinUSB.inf, the file must either be copied to Windows XP systems by the co-installer, or you should provide a separate decorated section for Windows XP.
USB_Install.HW: This section is the key in the .inf file. It specifies the device interface globally unique identifier (GUID) for your device. The AddReg directive sets the specified interface GUID in a standard registry value. When Winusb.sys is loaded as the device's function driver, it reads the registry value DeviceInterfaceGUIDs key and uses the specified GUID to represent the device interface. You should replace the GUID in this example with one that you create specifically for your device. If the protocols for the device change, create a new device interface GUID.
Note User-mode software must call SetupDiGetClassDevs to enumerate the registered device interfaces that are associated with one of the device interface classes specified under the DeviceInterfaceGUIDs key. SetupDiGetClassDevs returns the device handle for the device that the user-mode software must then pass to the WinUsb_Initialize routine to obtain a WinUSB handle for the device interface. For more info about these routines, see How to Access a USB Device by Using WinUSB Functions.
Omega Usb Devices Driver Adapter
The following INF installs WinUSB as the OSR USB FX2 board's function driver on a x64-based system. The example shows INF with WDF coinstallers.
USB_Install.CoInstallers: This section, which includes the referenced AddReg and CopyFiles sections, contains data and instructions to install the WinUSB and KMDF co-installers and associate them with the device. Most USB devices can use these sections and directives without modification.
The x86-based and x64-based versions of Windows have separate co-installers.
Note Each co-installer has free and checked versions. Use the free version to install WinUSB on free builds of Windows, including all retail versions. Use the checked version (with the '_chk' suffix) to install WinUSB on checked builds of Windows.
Each time Winusb.sys loads, it registers a device interface that has the device interface classes that are specified in the registry under the DeviceInterfaceGUIDs key.
Note If you use the redistributable WinUSB package for Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, make sure that you don't uninstall WinUSB in your uninstall packages. Other USB devices might be using WinUSB, so its binaries must remain in the shared folder.
How to create a driver package that installs Winusb.sys
To use WinUSB as the device's function driver, you create a driver package. The driver package must contain these files:
- WinUSB co-installer (Winusbcoinstaller.dll)
- KMDF co-installer (WdfcoinstallerXXX.dll)
- An .inf file that installs Winusb.sys as the device's function driver. For more information, see Writing an .Inf File for WinUSB Installation.
- A signed catalog file for the package. This file is required to install WinUSB on x64 versions of Windows starting with Vista.
Note Make sure that the driver package contents meet these requirements:
Omega Usb Devices Driver Updater
- The KMDF and WinUSB co-installer files must be obtained from the same version of the Windows Driver Kit (WDK).
- The co-installer files must be obtained from the latest version of the WDK, so that the driver supports all the latest Windows releases.
- The contents of the driver package must be digitally signed with a Winqual release signature. For more info about how to create and test signed catalog files, see Kernel-Mode Code Signing Walkthrough on the Windows Dev Center - Hardware site.
Omega Usb Devices Driver Win 7
Download the Windows Driver Kit (WDK) and install it.
Create a driver package folder on the machine that the USB device is connected to. For example, c:UsbDevice.
Copy the WinUSB co-installer (WinusbcoinstallerX.dll) from the WinDDKBuildNumberredistwinusb folder to the driver package folder.
The WinUSB co-installer (Winusbcoinstaller.dll) installs WinUSB on the target system, if necessary. The WDK includes three versions of the co-installer depending on the system architecture: x86-based, x64-based, and Itanium-based systems. They are all named WinusbcoinstallerX.dll and are located in the appropriate subdirectory in the WinDDKBuildNumberredistwinusb folder.
Copy the KMDF co-installer (WdfcoinstallerXXX.dll) from the WinDDKBuildNumberredistwdf folder to the driver package folder.
The KMDF co-installer (WdfcoinstallerXXX.dll) installs the correct version of KMDF on the target system, if necessary. The version of WinUSB co-installer must match the KMDF co-installer because KMDF-based client drivers, such as Winusb.sys, require the corresponding version of the KMDF framework to be installed properly on the system. For example, Winusbcoinstaller2.dll requires KMDF version 1.9, which is installed by Wdfcoinstaller01009.dll. The x86 and x64 versions of WdfcoinstallerXXX.dll are included with the WDK under the WinDDKBuildNumberredistwdf folder. The following table shows the WinUSB co-installer and the associated KMDF co-installer to use on the target system.
Use this table to determine the WinUSB co-installer and the associated KMDF co-installer.
WinUSB co-installer KMDF library version KMDF co-installer Winusbcoinstaller.dll Requires KMDF version 1.5 or later Wdfcoinstaller01005.dll
Wdfcoinstaller01007.dll
Wdfcoinstaller01009.dll
Winusbcoinstaller2.dll Requires KMDF version 1.9 or later Wdfcoinstaller01009.dll Winusbcoinstaller2.dll Requires KMDF version 1.11 or later WdfCoInstaller01011.dll Write an .inf file that installs Winusb.sys as the function driver for the USB device.
Create a signed catalog file for the package. This file is required to install WinUSB on x64 versions of Windows.
Attach the USB device to your computer.
Open Device Manager to install the driver. Follow the instructions on the Update Driver Software wizard and choose manual installation. You will need to provide the location of the driver package folder to complete the installation.
Related topics
WinUSB Architecture and Modules
Choosing a driver model for developing a USB client driver
How to Access a USB Device by Using WinUSB Functions
WinUSB Power Management
WinUSB Functions for Pipe Policy Modification
WinUSB Functions
WinUSB
